Wonders of Wildlife: Eastern Red Bat
Eastern Red Bat
Other Common Names: Red bat, Tree bat
Scientific Name: Lasiurus borealis
Found in Alabama: Common statewide
Diet: Carnivore (eats animals) |
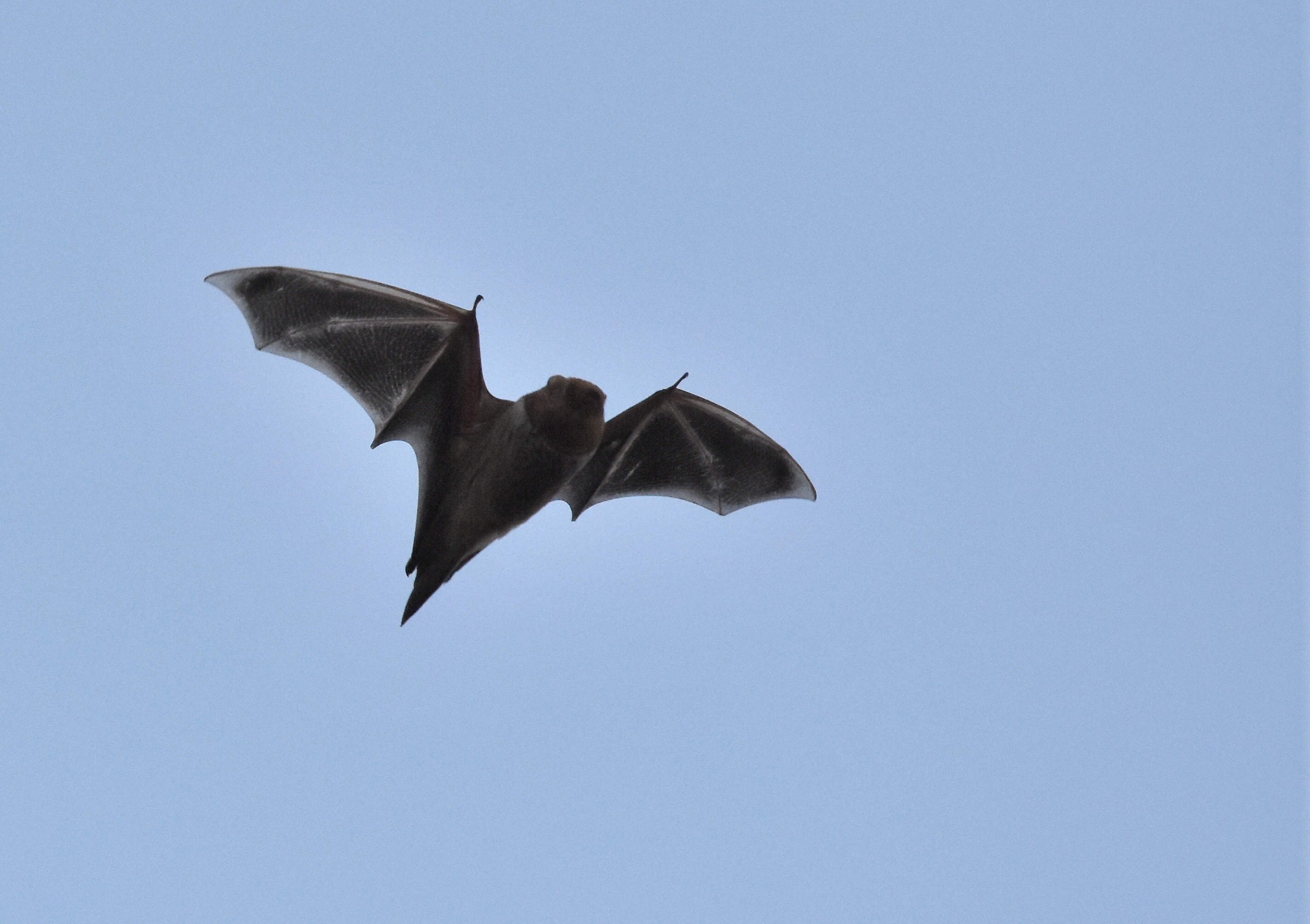
Eastern Red Bat in Flight
Wikimedia - Andy Reago and Chrissy McClarren
Click on image to enlarge it |
Learn more about...
 Watch our 3-minute video to learn about bat conservation and white-nose syndrome.
Watch our 3-minute video to learn about bat conservation and white-nose syndrome.
YouTube | Vimeo
| CLASSIFICATION |
|
What type of animal am I?
- I am a vertebrate (an animal with a spine or backbone).
- I am warm-blooded, so I can control my body temperature.
- I have hair/fur on the outside of my body that keep me warm.
- I breathe with lungs just like you.
- I have 2 legs.
- I have wings.
|
Scientists use basic traits to group animals into different taxonomic classes.
For a taxonomic classification chart comparing key traits of common backyard wildlife,
CLICK HERE! |
|
| The Eastern Red Bat is a MAMMAL! |
| IDENTIFICATION TIPS |
| |
|
|
Size: |
- Range from 3.5-4.5 inches long.
- Wingspan ranges from 11-13 inches
- Weigh less than an ounce
|
| |
|
Key Characteristics: |
- Range in coloration from bright orange-red to orange-brown
- Distinct section of white fur around the neck
- Have a white section of fur near fingertips
- Tips of hair have white coloration, giving them a "frosted" appearance.
- Females appear more pale in color than males.
|
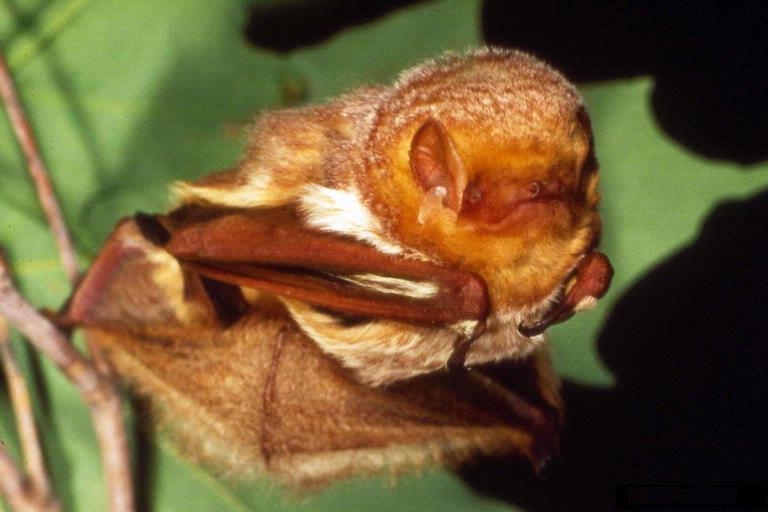
Eastern Red Bat
Wikimedia - Susan Ellis, Bugwoord.org
Click on image to enlarge it |
| |
|
|
Juveniles (young): |
- Young are similar in appearance to adults but are smaller in size.
|
| ADAPTATIONS |
| |
| PHYSICAL ADAPTATIONS |
| |
| Eastern Red Bats use echolocation: |
- Bats hunt for insects by a process called echolocation.
- During this process, the bats send out a series of high-pitched noises.
- These noises bounce off the insects and back to the bats.
- Bats are able to recognize these sounds and use the information to determine the location of the prey.
- They make different noises for activities such as searching for food, hunting, and social communication with other eastern red bats.
|
| |
| Eastern Red Bats can fly: |
- Bats are the only mammals capable of true flight.
- A bat's skeleton is lightweight and has special features for the powerful flight.
- The breastbone contains a keel (a strong bone to which the flight muscles connect).
- They also have a special membrane (thin layer of skin) connecting their long fingers to create the wing. This layer of skin is called the patagium.
- This membrane extends around the bat's tail which is used for steering, braking, and catching insects while flying.
|
| |
| Eastern Red Bats use camouflage: |
- Eastern red bats roost (a place where they rest) among the leaves of the trees within the forests.
- Their body size and coloration allow them to easily camouflage (ability to blend in with the surrounding environment) while hanging upside down from the branches.
- The red coloration resembles the dead leaves of elm, oak, and sycamore trees.
- By blending in to their surroundings, it makes it more difficult for them to be spotted by predators (animals that eat them).
|
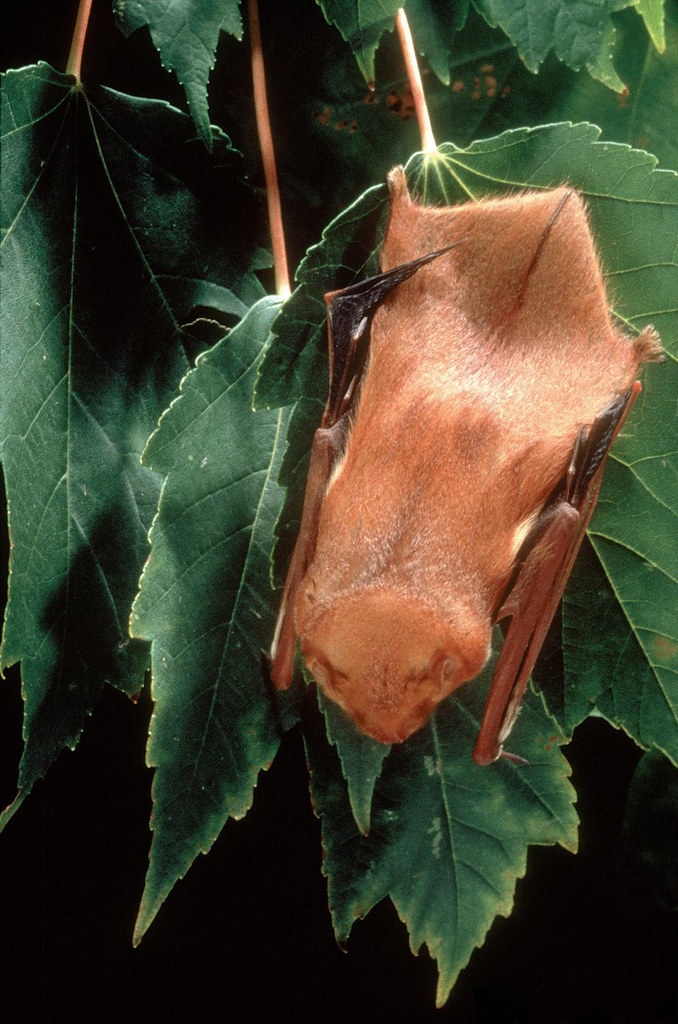
Eastern Red Bat Patagium
Flickr - U.S. Department of Agriculture
Click on image to enlarge it
|
| |
| |
| BEHAVIORAL ADAPTATIONS |
| |
| Eastern Red Bats are nocturnal: |
- They are active during the night (nocturnal).
|
| |
| Eastern Red Bats avoid cold weather: |
- Eastern red bats are migratory (moving to more northern locations during the spring and summer and traveling south during the colder months).
- Some individuals may stay in a northern part of their range and go to a state of hibernation (becoming dormant as if in a deep sleep) during the colder months.
- Their breathing, heart rate, and temperature are reduced during hibernation just like your breathing and heartbeat slows down while you are asleep.
- During this time, a bat will find a hollowed-out tree where they will be protected while they are not alert.
|
| LIFE CYCLE |
| |
|
|
| Life Cycle Stages of the Eastern Red Bat |
| |
|
|
Nest: |
- Females give birth in the roost (area where they rest) usually within tree branches.
|
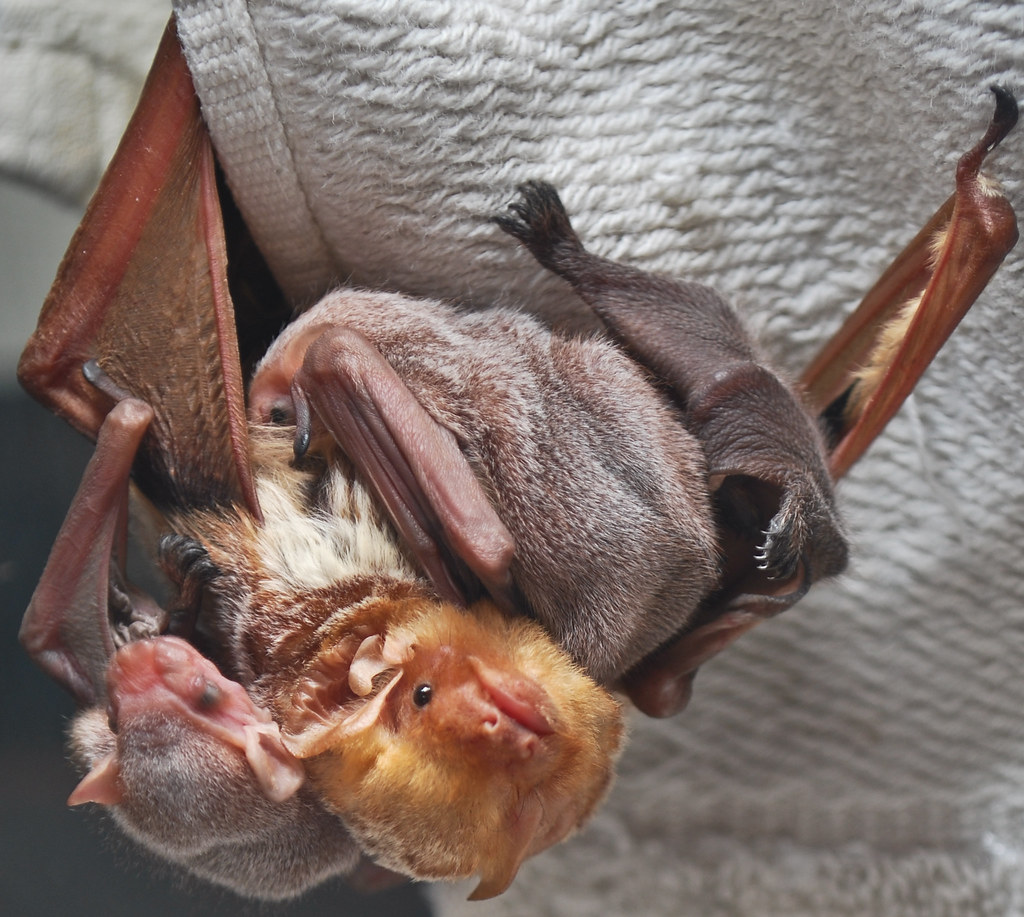
Eastern Red Bat with Babies
Flickr - Josh Henderson
Click on image to enlarge it |
| |
|
Young: |
- Females give birth to 1-4 young at a time in the spring.
- They can have up to two litters per year.
- When the young are born, they hang hang on to mother using their teeth or feet for around 5 weeks.
|
| |
|
|
Life Span: |
- Average life span is estimated to be around 8-10 years.
|
| NATURAL Habitat Needs |
ADULTS |
YOUNG |
| Food |
- Insectivores (eat insects).
- Feed on moths, beetles, mosquitoes, flies, cicadas, and other night-flying insects.
|
- Feed on milk from the mother for around 5 weeks until they are independent and can find food on their own.
|
| Water |
- Drink from sources of fresh water such as a stream, pond, or lake.
|
- Obtain hydration from the mother until they are independent.
|
| Shelter |
- Commonly found in hardwood, pine, and mixed forests.
- Prefer to live near forest edges.
- They roost within the leaves of the trees like sweetgum, elm, maple, and oak.
- They will also roost in Spanish moss.
|
- Female will carry the young around until they are independent and can forage on their own, usually around 5 weeks.
|
| Places to Raise Young |
- Mother will keep young with her for a few weeks until they are independent.
- She will leave them in the roost while she is out hunting insects at night.
|
|
BACKYARD
Habitat Needs |
ADULTS |
YOUNG |
| Food |
- Plant native grasses and wildflowers that attract moths, beetles, mosquitoes, flies, cicadas, and other night-flying insects.
- Do not spray pesticides that might harm insect populations.
|
- Providing resources for the mother will indirectly benefit the young.
|
| Water |
- If a fresh source of water is not located nearby, provide a source of fresh water such as a bird bath.
|
| Shelter |
- Do not remove mature, large trees or tree snags (dead or dying trees), or leaf litter which provide safe locations for roosting.
|
| Places to Raise Young |
- Do not remove large trees, tree snags, or leaf litter.
|
|
| ECOLOGICAL ROLE |
| |
|
| Animals play an important ecological role in the health of habitats and ecosystems. |
| |
|
|
Food Source:
|
- Young eastern red bats are sometimes eaten by blue jays.
- Adult eastern red bats are a food source for sharp-shinned hawks, American kestrels, great horned owls, opossums, foxes, and snakes, especially if they hibernate (become dormant as if in a deep sleep) too close to the ground.
|
| |
|
Insect Control: |
- Eastern red bats are insectivores (eat insects) and consume a large number of night-flying insects.
- Bats are beneficial to humans because they help control populations of the insects they eat.
- This includes mosquitoes which can carry diseases such as West Nile and malaria that can be transmitted to humans.
- Bats also play a role in controlling populations of insects that cause damage to crops.
|
INFORMATION SOURCES FOR THIS SPECIES
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Best, T. L. and J. L. Dusi. 2014
Mammals of Alabama
The University of Alabama Press
|
.





 Wildlife Tag
Wildlife Tag